Health Monitoring System
Introduction
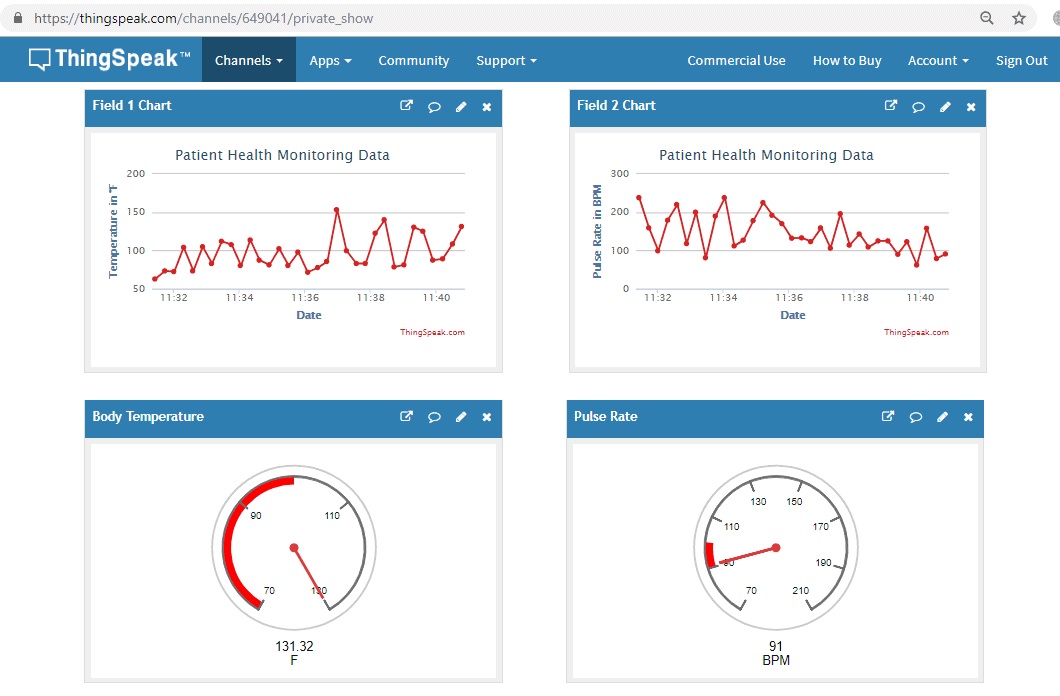
The IoT Based Patient Health Monitoring System using ESP8266 & Arduino. The IoT platform used in this project is ThingSpeak. ThingSpeak is an open-source Internet of Things (IoT) application and API to store and retrieve data from things using the HTTP protocol over the Internet or via a Local Area Network. This IoT device could read the beats rate and measure the surrounding temperatureerature. It continuously monitors the beats rate and surrounding temperatureerature and updates them to an IoT platform.
Components
Before you start building your Arduino-based drone, make sure you have the following components:
Arduino Nano Board
ESP8266-01 WiFi Module
16x2 LCD Display
Potentiometer 10K
Beats Sensor
LM35 Temperatureerature Sensor
2K Resistor
1K Resistor
LED 5mm Any Color
Connecting Wires
Breadboard
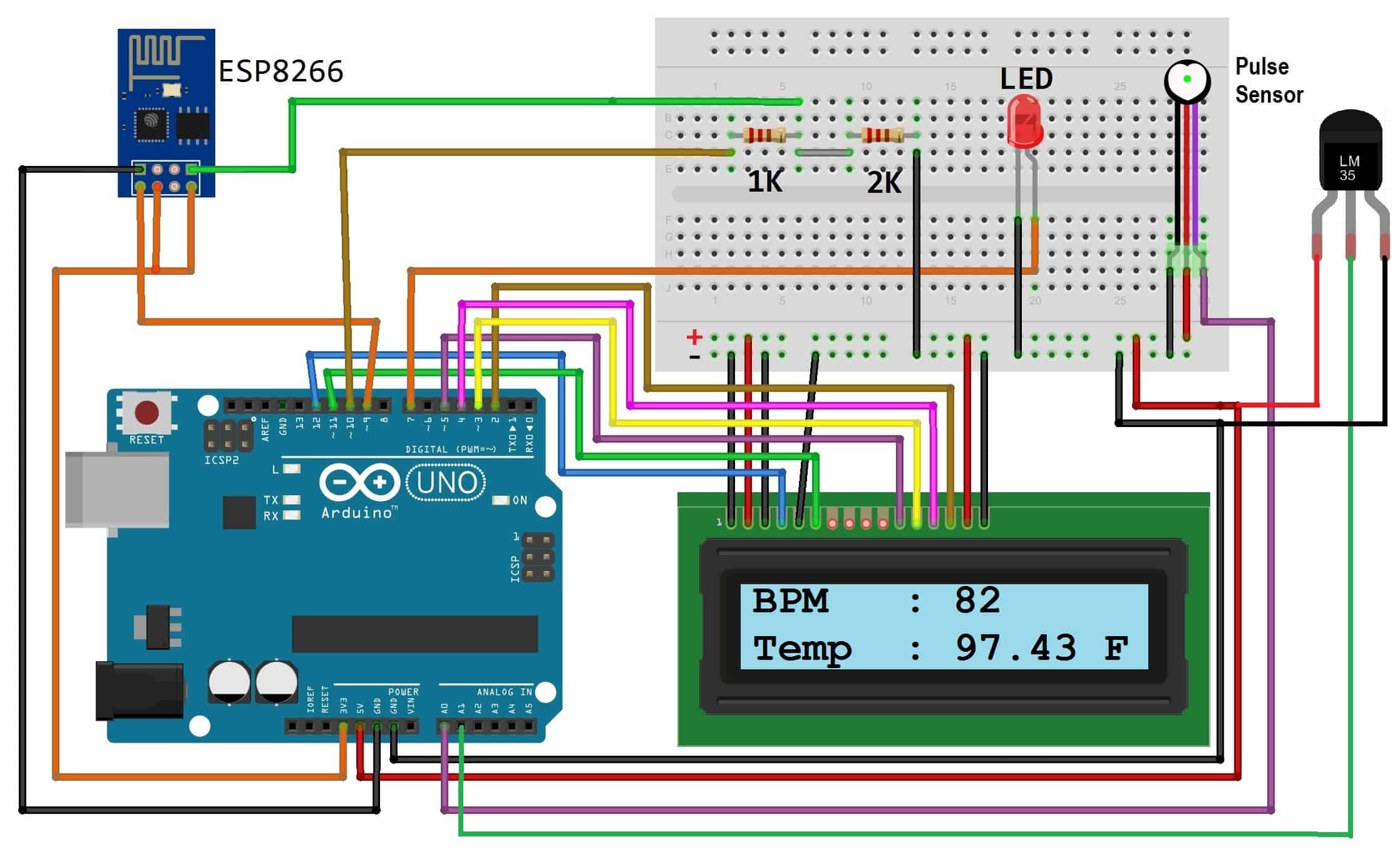
Circuit diagram
1. Connect Beats Sensor output pin to A0 of Arduino and other two pins to VCC & GND.
2. Connect LM35 Temperatureerature Sensor output pin to A1 of Arduino and other two pins to VCC & GND.
3. Connect the LED to Digital Pin 7 of Arduino via a 220-ohm resistor.
4. Connect Pin 1,3,5,16 of LCD to GND.
5. Connect Pin 2,15 of LCD to VCC.
6. Connect Pin 4,6,11,12,13,14 of LCD to Digital Pin12,11,5,4,3,2 of Arduino.
7. The RX pin of ESP8266 works on 3.3V and it will not communicate with the Arduino when we will connect it directly to the Arduino. So, we will have to make a voltage divider for it which will convert the 5V into 3.3V. This can be done by connecting the 2.2K & 1K resistor. Thus the RX pin of the ESP8266 is connected to pin 10 of Arduino through the resistors.
8. Connect the TX pin of the ESP8266 to pin 9 of the Arduino.
IoT Based Patient Health Monitoring System using ESP8266 & Arduino as shown in the figure here.
Code
#include
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
#include
float beats = 0;
float temperature = 0;
SoftwareSerial ser(9,10);
String apiKey = "OO707TGA1BLUNN12";
// Variables
int beatsPin = A0; // Beats Sensor purple wire connected to analog pin 0
int blinkPin = 7 ; // pin to blink led at each beat
int fadePin = 13; // pin to do fancy classy fading blink at each beat
int fadeRate = 0; // used to fade LED on with PWM on fadePin
// Volatile Variables, used in the interrupt service routine!
volatile int bpm; // int that holds raw Analog in 0. updated every 2mS
volatile int signal; // holds the incoming raw data
volatile int IBI = 600; // int that holds the time interval between beats! Must be seeded!
volatile boolean Beats = false; // "True" when User's live heartbeat is detected. "False" when nota "live beat".
volatile boolean QS = false; // becomes true when Arduoino finds a beat.
// Regards Serial OutPut -- Set This Up to your needs
static boolean serialVisual = true; // Set to 'false' by Default. Re-set to 'true' to see Arduino Serial Monitor ASCII Visual Beats
volatile int rate[10]; // array to hold last ten IBI values
volatile unsigned long sampleCounter = 0; // used to determine beats timing
volatile unsigned long lastBeatTime = 0; // used to find IBI
volatile int P = 512; // used to find peak in beats wave, seeded
volatile int T = 512; // used to find trough in beats wave, seeded
volatile int thresh = 525; // used to find instant moment of heart beat, seeded
volatile int amp = 100; // used to hold amplitude of beats waveform, seeded
volatile boolean firstBeat = true; // used to seed rate array so we startup with reasonable BPM
volatile boolean secondBeat = false; // used to seed rate array so we startup with reasonable BPM
void setup()
{
lcd.begin(16, 2);
pinMode(blinkPin,OUTPUT); // pin that will blink to your heartbeat!
pinMode(fadePin,OUTPUT); // pin that will fade to your heartbeat!
Serial.begin(115200); // we agree to talk fast!
interruptSetup(); // sets up to read Beats Sensor signal every 2mS
// IF YOU ARE POWERING The Beats Sensor AT VOLTAGE LESS THAN THE BOARD VOLTAGE,
// UN-COMMENT THE NEXT LINE AND APPLY THAT VOLTAGE TO THE A-REF PIN
// analogReference(EXTERNAL);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print(" Patient Health");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print(" Monitoring ");
delay(4000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Initializing....");
delay(5000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("Getting Data....");
ser.begin(9600);
ser.println("AT");
delay(1000);
ser.println("AT+GMR");
delay(1000);
ser.println("AT+CWMODE=3");
delay(1000);
ser.println("AT+RST");
delay(5000);
ser.println("AT+CIPMUX=1");
delay(1000);
String cmd="AT+CWJAP=\"Alexahome\",\"98765432\"";
ser.println(cmd);
delay(1000);
ser.println("AT+CIFSR");
delay(1000);
}
// Where the Magic Happens
void loop()
{
serialOutput();
if (QS == true) // A Heartbeat Was Found
{
// BPM and IBI have been Determined
// Quantified Self "QS" true when arduino finds a heartbeat
fadeRate = 255; // Makes the LED Fade Effect Happen, Set 'fadeRate' Variable to 255 to fade LED with beats
serialOutputWhenBeatHappens(); // A Beat Happened, Output that to serial.
QS = false; // reset the Quantified Self flag for next time
}
ledFadeToBeat(); // Makes the LED Fade Effect Happen
delay(20); // take a break
read_temperature();
esp_8266();
}
void ledFadeToBeat()
{
fadeRate -= 15; // set LED fade value
fadeRate = constrain(fadeRate,0,255); // keep LED fade value from going into negative numbers!
analogWrite(fadePin,fadeRate); // fade LED
}
void interruptSetup()
{
// Initializes Timer2 to throw an interrupt every 2mS.
TCCR2A = 0x02; // DISABLE PWM ON DIGITAL PINS 3 AND 11, AND GO INTO CTC MODE
TCCR2B = 0x06; // DON'T FORCE COMPARE, 256 PRESCALER
OCR2A = 0X7C; // SET THE TOP OF THE COUNT TO 124 FOR 500Hz SAMPLE RATE
TIMSK2 = 0x02; // ENABLE INTERRUPT ON MATCH BETWEEN TIMER2 AND OCR2A
sei(); // MAKE SURE GLOBAL INTERRUPTS ARE ENABLED
}
void serialOutput()
{ // Decide How To Output Serial.
if (serialVisual == true)
{
arduinoSerialMonitorVisual('-', Signal); // goes to function that makes Serial Monitor Visualizer
}
else
{
sendDataToSerial('S', Signal); // goes to sendDataToSerial function
}
}
void serialOutputWhenBeatHappens()
{
if (serialVisual == true) // Code to Make the Serial Monitor Visualizer Work
{
Serial.print("*** Heart-Beat Happened *** "); //ASCII Art Madness
Serial.print("BPM: ");
Serial.println(BPM);
}
else
{
sendDataToSerial('B',BPM); // send heart rate with a 'B' prefix
sendDataToSerial('Q',IBI); // send time between beats with a 'Q' prefix
}
}
void arduinoSerialMonitorVisual(char symbol, int data )
{
const int sensorMin = 0; // sensor minimum, discovered through experiment
const int sensorMax = 1024; // sensor maximum, discovered through experiment
int sensorReading = data; // map the sensor range to a range of 12 options:
int range = map(sensorReading, sensorMin, sensorMax, 0, 11);
// do something different depending on the
// range value:
switch (range)
{
case 0:
Serial.println(""); /////ASCII Art Madness
break;
case 1:
Serial.println("---");
break;
case 2:
Serial.println("------");
break;
case 3:
Serial.println("---------");
break;
case 4:
Serial.println("------------");
break;
case 5:
Serial.println("--------------|-");
break;
case 6:
Serial.println("--------------|---");
break;
case 7:
Serial.println("--------------|-------");
break;
case 8:
Serial.println("--------------|----------");
break;
case 9:
Serial.println("--------------|----------------");
break;
case 10:
Serial.println("--------------|-------------------");
break;
case 11:
Serial.println("--------------|-----------------------");
break;
}
}
void sendDataToSerial(char symbol, int data )
{
Serial.print(symbol);
Serial.println(data);
}
ISR(TIMER2_COMPA_vect) //triggered when Timer2 counts to 124
{
cli(); // disable interrupts while we do this
signal = analogRead(beatsPin); // read the Beats Sensor
sampleCounter += 2; // keep track of the time in mS with this variable
int N = sampleCounter - lastBeatTime; // monitor the time since the last beat to avoid noise
// find the peak and trough of the beats wave
if(signal < thresh && N > (IBI/5)*3) // avoid dichrotic noise by waiting 3/5 of last IBI
{
if (signal < T) // T is the trough
{
T = signal; // keep track of lowest point in beats wave
}
}
if(signal > thresh && signal > P)
{ // thresh condition helps avoid noise
P = signal; // P is the peak
} // keep track of highest point in beats wave
// NOW IT'S TIME TO LOOK FOR THE HEART BEAT
// signal surges up in value every time there is a beats
if (N > 250)
{ // avoid high frequency noise
if ( (signal > thresh) && (Beats == false) && (N > (IBI/5)*3) )
{
Beats = true; // set the Beats flag when we think there is a beats
digitalWrite(blinkPin,HIGH); // turn on pin 13 LED
IBI = sampleCounter - lastBeatTime; // measure time between beats in mS
lastBeatTime = sampleCounter; // keep track of time for next beats
if(secondBeat)
{ // if this is the second beat, if secondBeat == TRUE
secondBeat = false; // clear secondBeat flag
for(int i=0; i<=9; i++) // seed the running total to get a realisitic BPM at startup
{
rate[i] = IBI;
}
}
if(firstBeat) // if it's the first time we found a beat, if firstBeat == TRUE
{
firstBeat = false; // clear firstBeat flag
secondBeat = true; // set the second beat flag
sei(); // enable interrupts again
return; // IBI value is unreliable so discard it
}
// keep a running total of the last 10 IBI values
word runningTotal = 0; // clear the runningTotal variable
for(int i=0; i<=8; i++)
rate[i] = rate[i+1]; // and drop the oldest IBI value
runningTotal += rate[i]; // add up the 9 oldest IBI values
}
rate[9] = IBI; // add the latest IBI to the rate array
runningTotal += rate[9]; // add the latest IBI to runningTotal
runningTotal /= 10; // average the last 10 IBI values
BPM = 60000/runningTotal; // how many beats can fit into a minute? that's BPM!
QS = true; // set Quantified Self flag
// QS FLAG IS NOT CLEARED INSIDE THIS ISR
beats = BPM;
}
}
if (Signal < thresh && Beats == true)
{ // when the values are going down, the beat is over
digitalWrite(blinkPin,LOW); // turn off pin 13 LED
Beats = false; // reset the Beats flag so we can do it again
amp = P - T; // get amplitude of the beats wave
thresh = amp/2 + T; // set thresh at 50% of the amplitude
P = thresh; // reset these for next time
T = thresh;
}
if (N > 2500)
{ // if 2.5 seconds go by without a beat
thresh = 512; // set thresh default
P = 512; // set P default
T = 512; // set T default
lastBeatTime = sampleCounter; // bring the lastBeatTime up to date
firstBeat = true; // set these to avoid noise
secondBeat = false; // when we get the heartbeat back
}
sei(); // enable interrupts when youre done!
}// end isr
void esp_8266()
{
// TCP connection AT+CIPSTART=4,"TCP","184.106.153.149",80
String cmd = "AT+CIPSTART=4,\"TCP\",\"";
cmd += "184.106.153.149"; // api.thingspeak.com
cmd += "\",80";
ser.println(cmd);
Serial.println(cmd);
if(ser.find("Error"))
{
Serial.println("AT+CIPSTART error");
return;
}
String getStr = "GET /update?api_key=";
getStr += apiKey;
getStr +="&field1=";
getStr +=String(temperature);
getStr +="&field2=";
getStr +=String(beats);
getStr += "\r\n\r\n";
// send data length
cmd = "AT+CIPSEND=4,";
cmd += String(getStr.length());
ser.println(cmd);
Serial.println(cmd);
delay(1000);
ser.print(getStr);
Serial.println(getStr); //thingspeak needs 15 sec delay between updates
delay(3000);
}
void read_temperature()
{
int temperature_val = analogRead(A1);
float mv = (temperature_val/1024.0)*5000;
float cel = mv/10;
temperature = (cel*9)/5 + 32;
Serial.print("Temperatureerature:");
Serial.println(temperature);
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print("BPM :");
lcd.setCursor(7,0);
lcd.print(BPM);
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Temperature.:");
lcd.setCursor(7,1);
lcd.print(temperature);
lcd.setCursor(13,1);
lcd.print("F");
}